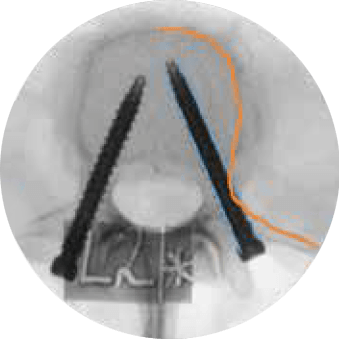
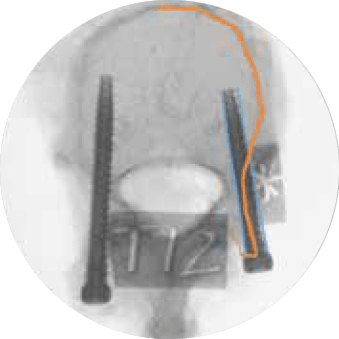
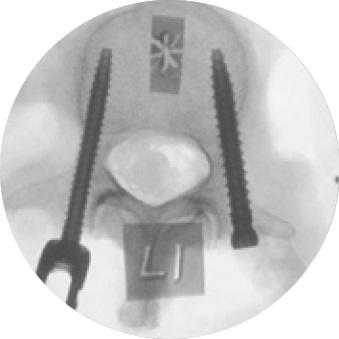
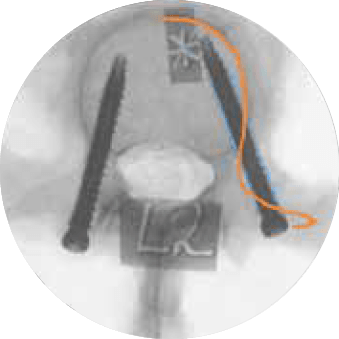
There is robotic navigation…
THEN THERE IS ExcelsiusGPS®
Request the ExcelsiusGPS® White Paper

Improving Screw Accuracy and Reducing Overall Procedural Time in a Cadaveric Setting with the Robotic Navigation Platform
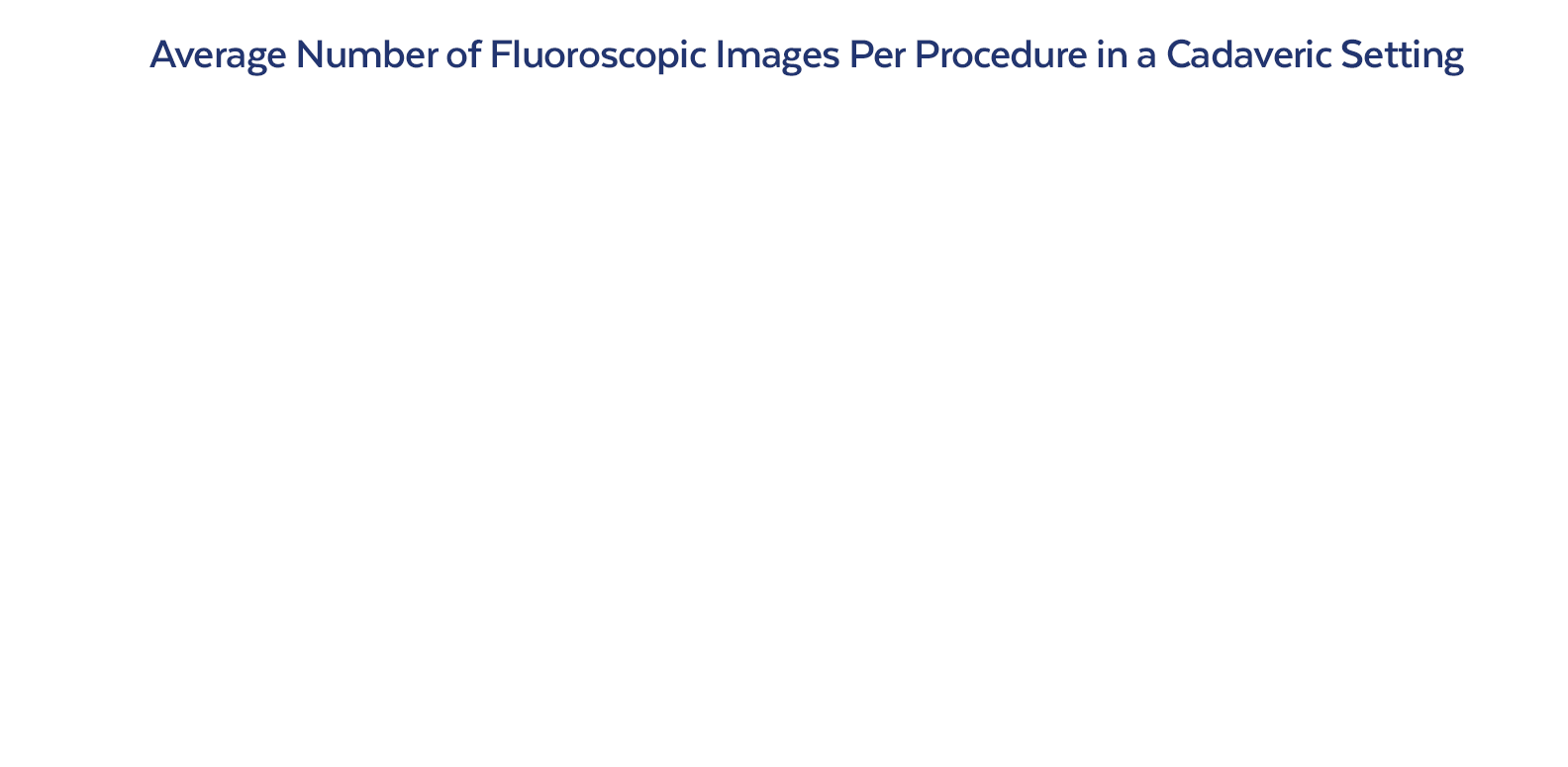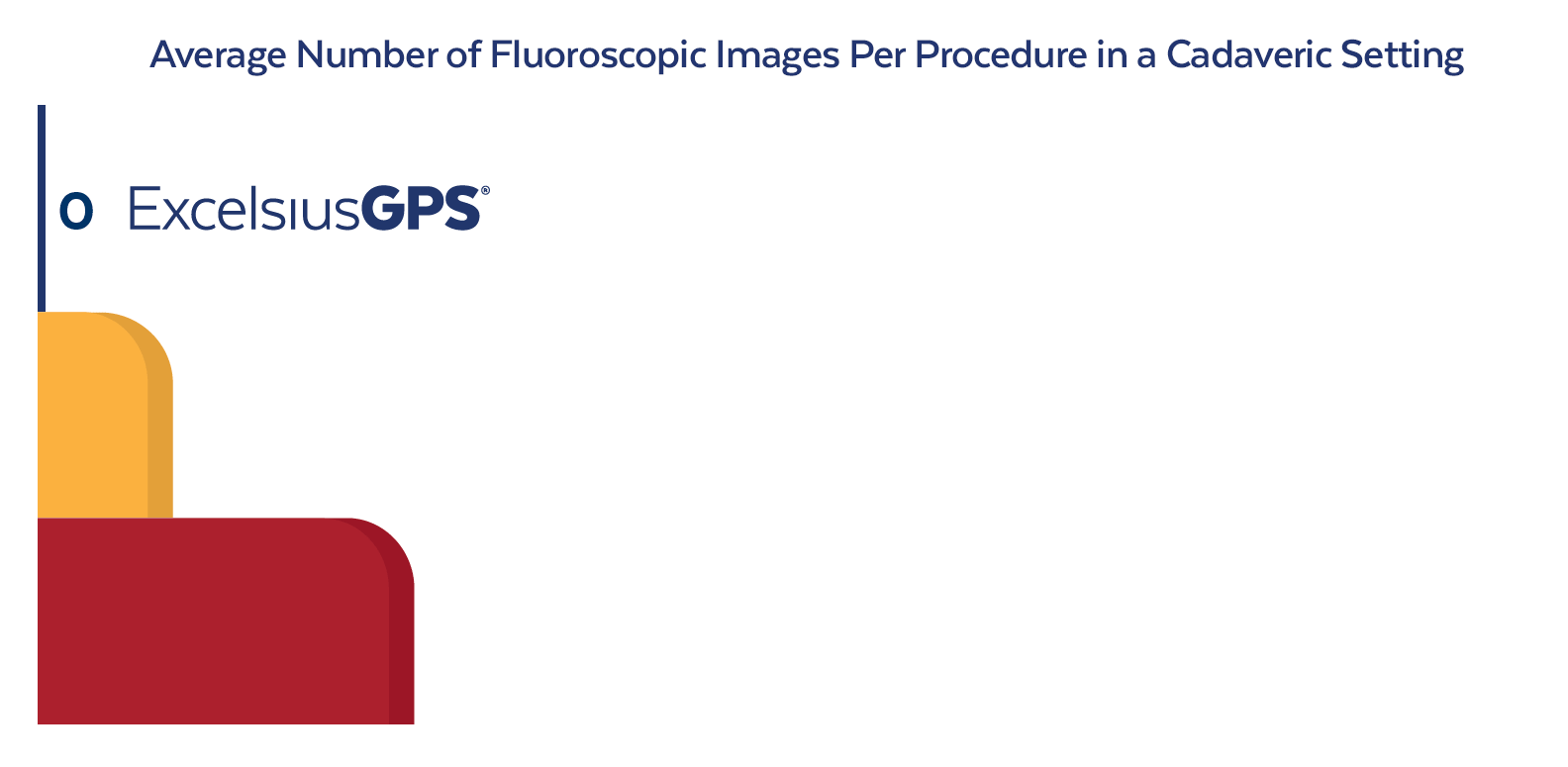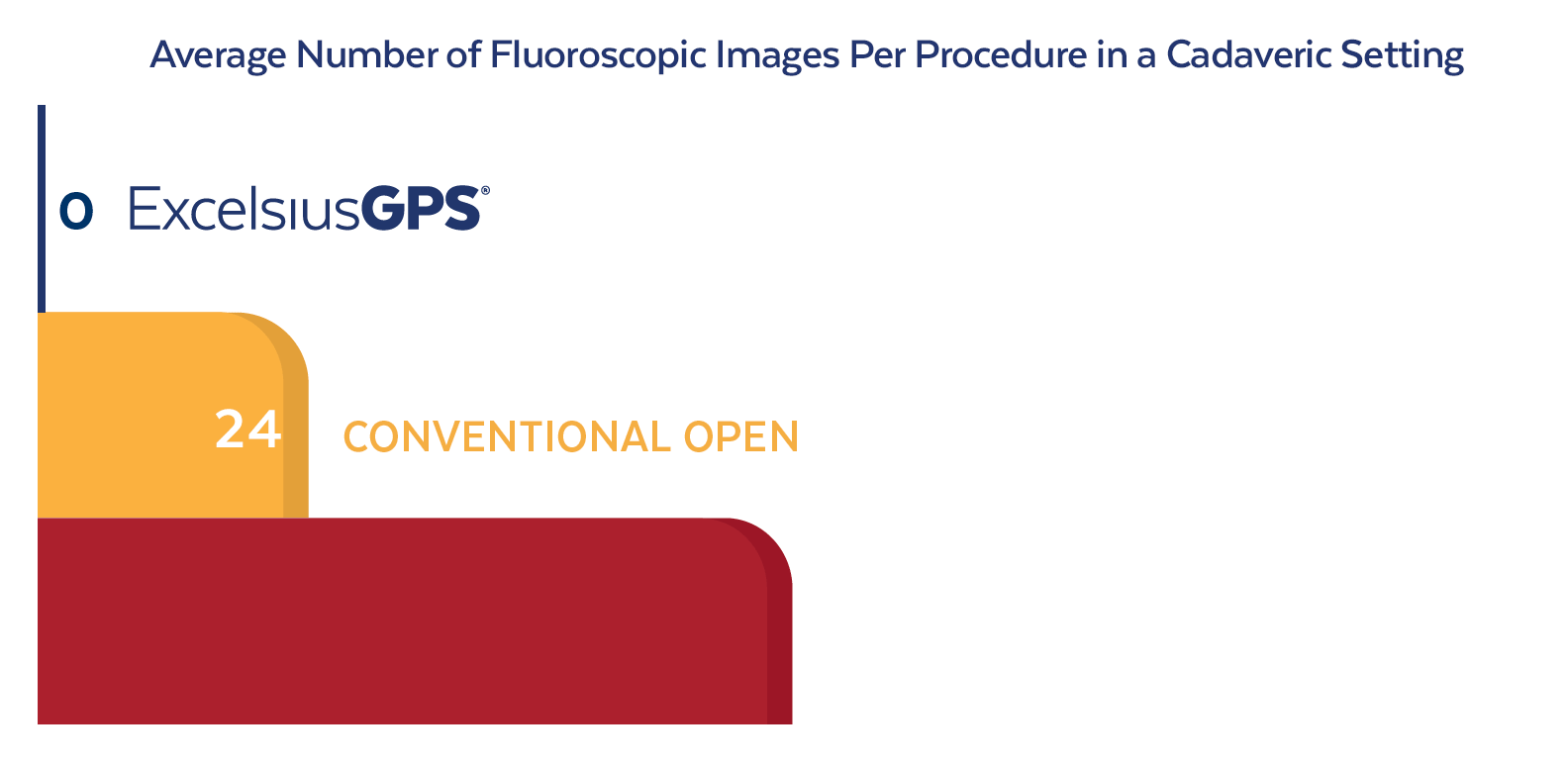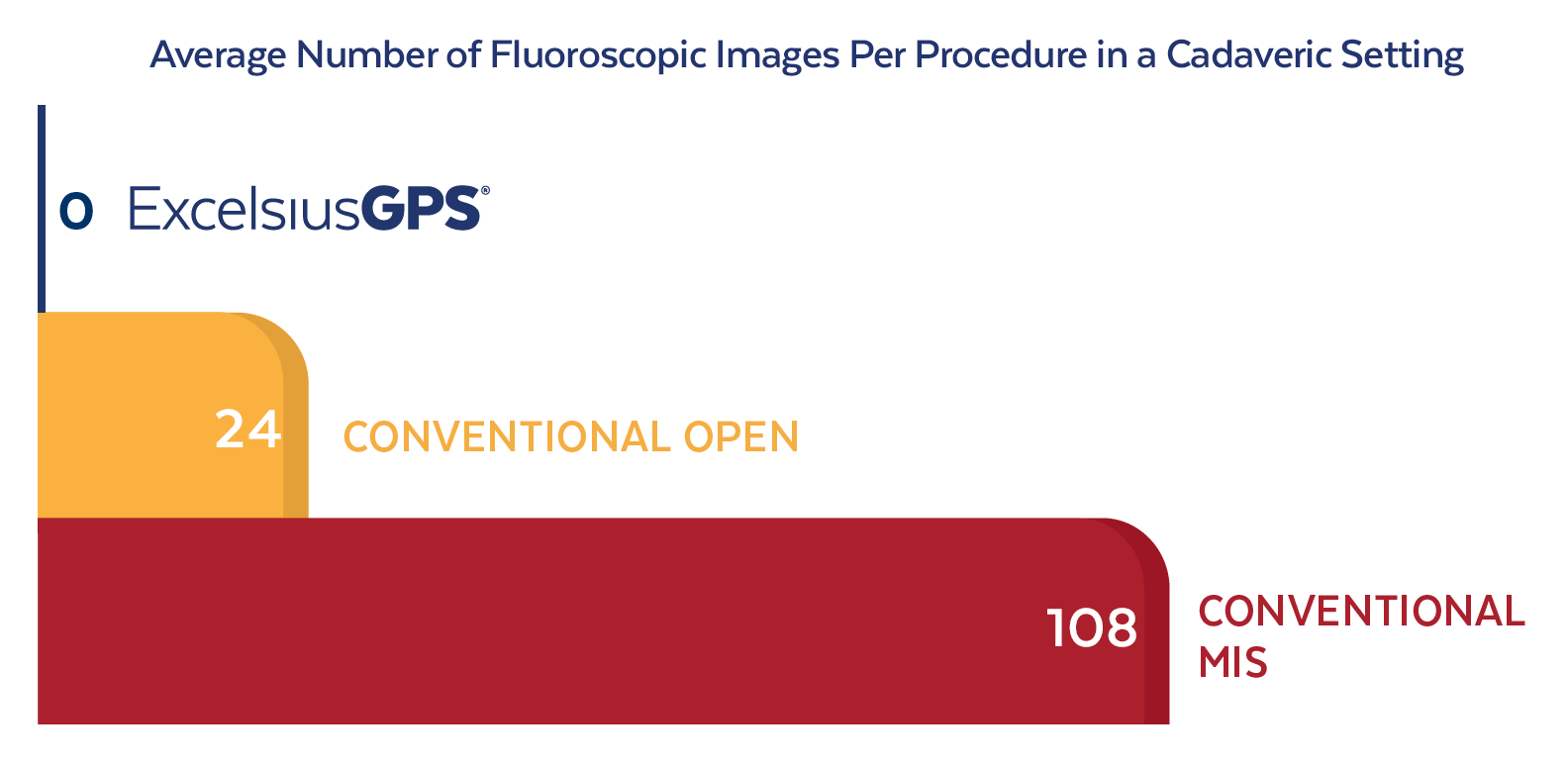
In a cadaveric study evaluating pedicle screw placement accuracy, placement time, and radiation dose, 10 surgeons with 2-23 years of experience placed a total of 160 pedicle screws with ExcelsiusGPS® and conventional techniques across MIS and open approaches. The use of ExcelsiusGPS® demonstrated:
Vaccaro, A. R. et al. ExcelsiusGPS® Robotic Navigation Platform Improves Screw Accuracy and Reduces Radiation Exposure Compared to Conventional Fluoroscopic Techniques in a Simulated Surgical Model. White paper (GMWP51). Globus Medical, Inc. (April 2018).
Improving Screw Placement Accuracy
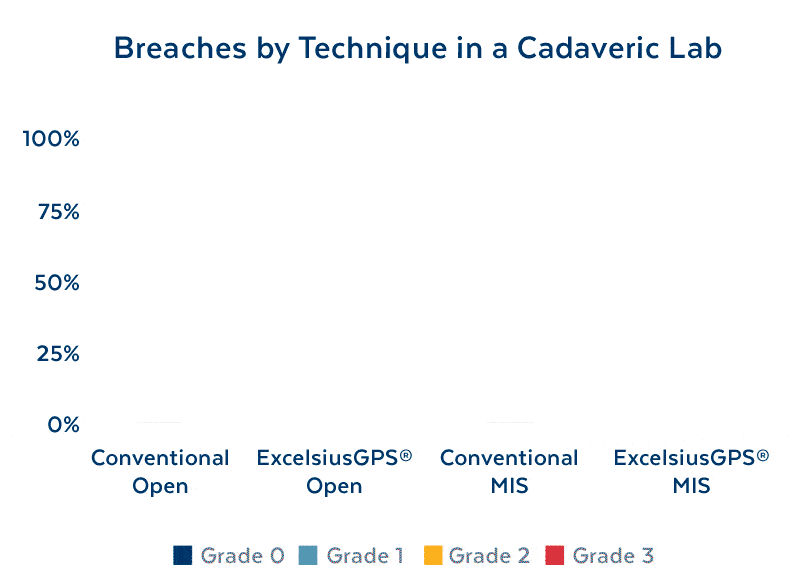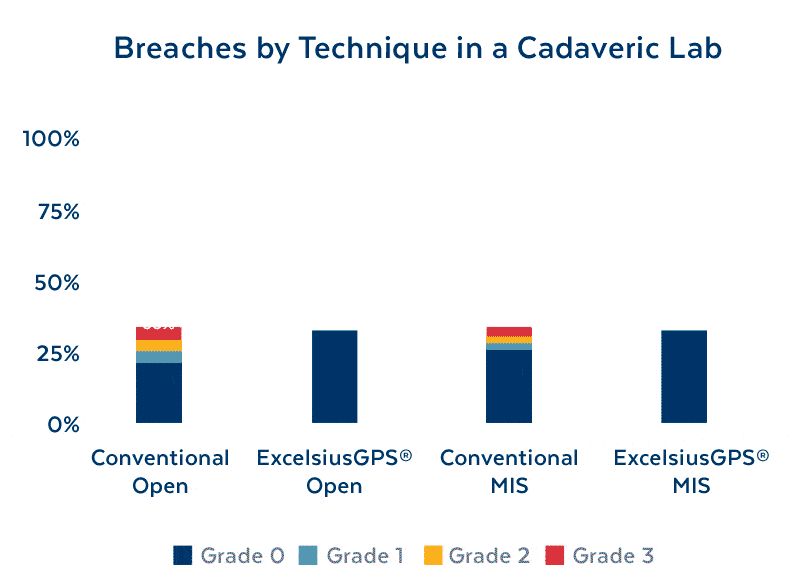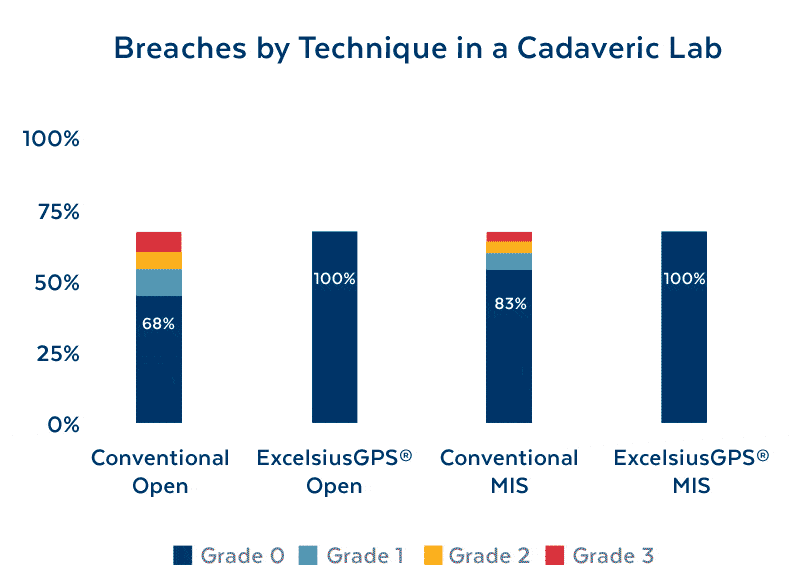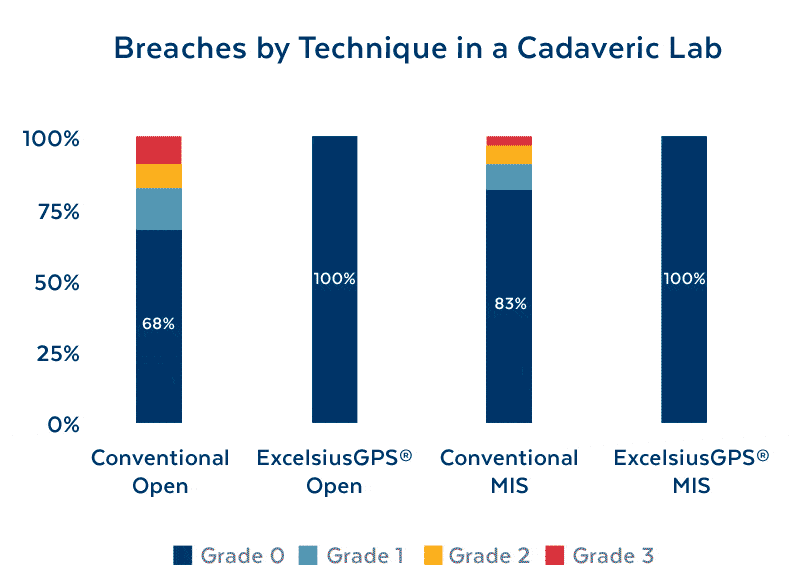
Reducing Radiation Exposure
Increasing MIS Efficiency
Overall Procedure Time
Screw Placement Time
ExcelsiusGPS® Robotic Navigation significantly reduced the duration of screw insertion in a cadaveric setting, averaging 3.6 minutes per screw compared to the conventional MIS average of 7.7 minutes per screw.